Sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL) is a prevalent condition affecting millions worldwide, characterized by damage to the inner ear or nerve pathways from the inner ear to the brain. Understanding its nuances is the first step toward managing its impact.
This blog post delves into various strategies to restore hearing function, offering hope and actionable advice for those navigating the challenges of SNHL.
Understanding Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Sensorineural hearing loss is primarily caused by damage to the hair cells in the cochlea or the auditory nerve. Factors contributing to this condition include aging, exposure to loud noise, certain medications, and various health conditions.
Unlike conductive auditory loss, which can often be corrected medically or surgically, SNHL is usually permanent. The key to managing it effectively lies in early diagnosis and intervention, which can significantly improve quality of life for those affected.
Lifestyle Adjustments to Support Hearing Restoration
Living with SNHL requires adjustments to minimize its impact on daily life. Protecting your ears from loud noises by wearing earplugs or earmuffs can prevent further damage. Regular auditory check-ups are crucial for monitoring the condition and adjusting to changes in hearing ability.
Additionally, engaging in activities that improve cognitive skills, like puzzles or learning a new language, can help the brain better process the sounds it receives, partially offsetting the effects of auditory loss.
Exploring Technological Solutions for Hearing Enhancement
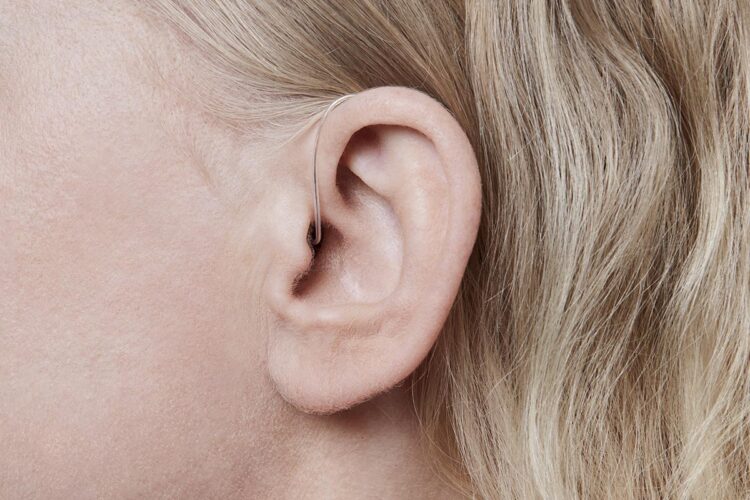
Technological advancements such as Starkey hearing aids have revolutionized the management of SNHL. Hearing aids are the most common tool, amplifying sounds to assist the damaged ears in processing audio. Cochlear implants are another option, bypassing damaged parts of the ear to directly stimulate the auditory nerve.
Additionally, assistive listening devices and apps can enhance the listening experience in challenging environments, making technology a cornerstone of modern SNHL management.
Dietary and Nutritional Considerations for Hearing Health
Nutrition plays a vital role in auditory health. Research suggests that a diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and certain vitamins can help protect against hearing loss. Foods like fish, nuts, fruits, and vegetables support ear health by combating oxidative stress and inflammation, potentially slowing the progression of SNHL.
While no diet can cure auditory loss, proper nutrition can bolster overall ear health and function.
Strategies for Effective Communication with Sensorineural Hearing Loss

Effective communication is crucial for individuals with SNHL. This involves both the speaker and the listener playing active roles. For the listener, it’s important to face the speaker, minimize background noise, and consider using auditory assistive technology.
Speakers can help by speaking clearly, not covering their mouths, and being patient. Visual cues and written communication are also valuable tools, ensuring that messages are conveyed and understood despite hearing challenges.
Seeking Professional Help: Treatment Options and Therapies
Professional guidance is essential in managing SNHL. Audiologists can recommend appropriate auditory aids, while otolaryngologists may explore if cochlear implants are suitable. Speech therapy can also be beneficial, helping individuals adapt to hearing aids and cochlear implants, ensuring they get the most out of these devices.
Regular consultations with auditory health professionals can lead to personalized strategies that significantly improve communication abilities and overall quality of life.
Holistic Approaches to Enhance Auditory Function
In addition to medical treatments, holistic approaches can support hearing health. Practices such as yoga and meditation may improve blood flow to the ears, potentially supporting auditory function. Mindfulness can also reduce stress, which is beneficial since stress can exacerbate hearing loss symptoms.
While these methods cannot reverse SNHL, they can complement traditional treatments, offering a comprehensive approach to managing auditory loss and enhancing overall well-being.
Conclusion
Sensorineural hearing loss presents challenges, but with the right strategies, individuals can lead fulfilling lives. From technological aids to dietary adjustments and holistic practices, a multifaceted approach can make a significant difference.
Embracing these tips and seeking professional advice can help restore auditory function and improve quality of life for those affected by SNHL.
 Hi Boox Popular Magazine 2024
Hi Boox Popular Magazine 2024



