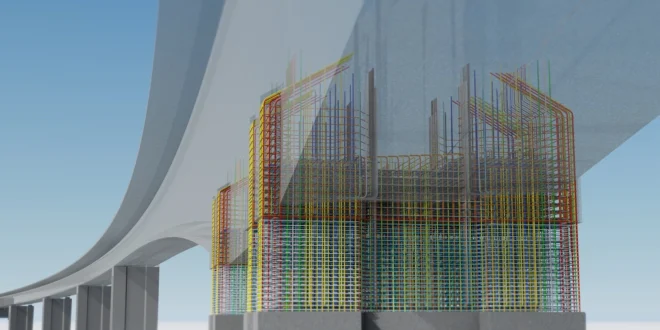
Building Information Modeling (BIM) is a technological process used in AEC (architecture, engineering, and construction) industries that allows digital representation of physical and functional characteristics of buildings. This post will explore advanced strategies for leveraging BIM to its fullest potential.
The upcoming sections will delve into ten specific tactics — such as AR implementations from XYZ Reality — and workflows that can enhance the efficiency of design and construction processes, reinforce collaboration among stakeholders, and support more informed decision-making.
What is BIM?
BIM is an integrated method of design, construction, and management for infrastructure projects. Here are key aspects that define BIM:
- Digital representation ─ BIM encapsulates comprehensive digital illustrations of a building’s physical and functional traits. It’s more than just 3D design; it can include 4D (time) and 5D (cost) elements.
- Collaboration tool ─ BIM promotes multidisciplinary collaboration, enabling AEC professionals to work together efficiently on a single platform.
- Information database ─ It serves as a rich information repository, housing data related to various stages of a building’s life cycle, from conception through demolition.
- Simulation and analysis ─ BIM allows simulation and analysis of various elements such as structural integrity, energy performance, and light analysis before construction begins.
- Facility management ─ Post-construction, BIM can be used for facility management, maintenance scheduling, and space management.
Understanding BIM is a prerequisite to exploring advanced strategies for leveraging its extensive potential.
10 Strategies for Advanced BIM
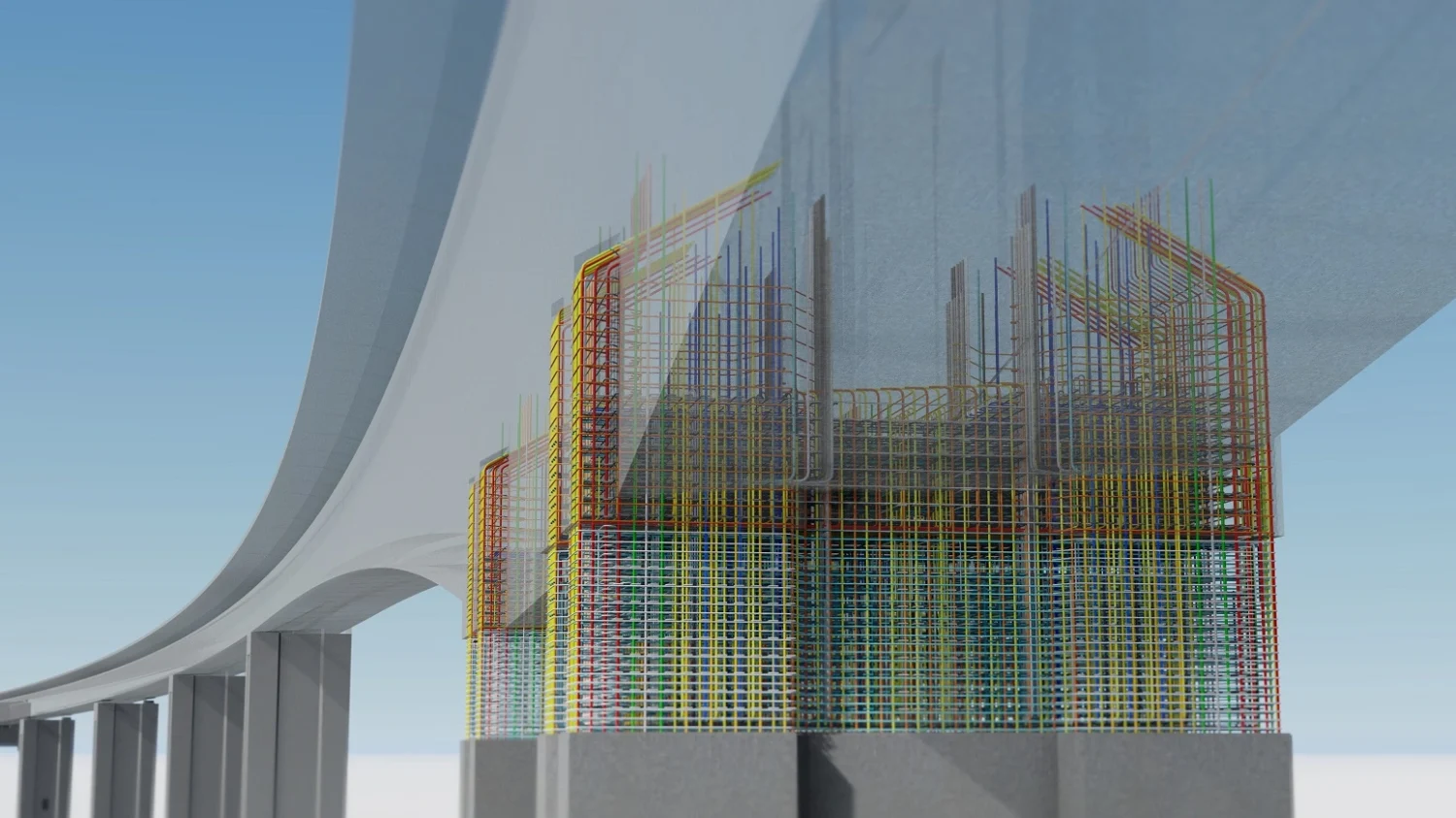
Here are some strategies to help you take your BIM utilization to the next level.
1. Implementing augmented reality (AR)
AR technology can be utilized to visualize BIM data in its original, real-world context — providing a more immersive and interactive experience for designers, clients, and other stakeholders. By overlaying digital 3D models onto physical spaces, AR can help identify potential design conflicts or issues early in the process, saving time and resources.
2. Utilizing automated clash detection
This strategy involves using BIM software to automatically detect clashes or conflicts in the design before construction begins. By catching these issues early, teams can avoid costly fixes down the line.
3. Integrating the Internet of Things (IoT)
IoT-empowered devices can gather real-time data from various sensors and devices installed within buildings, making this technology useful in providing real-time updates. This data can feed into the BIM model, enabling predictive maintenance and smarter energy management.
4. Leveraging machine learning (ML)
ML algorithms can be used to analyze BIM data and generate insights that human experts might overlook. This can support more informed decision-making and potentially uncover innovative design and construction solutions.
5. Adopting cloud-based BIM
Cloud technology allows for real-time BIM data sharing and collaboration among team members, regardless of their location. Updating the information regularly — it can help streamline workflows, enhance communication and ensure everyone always works from up-to-date information.
6. Incorporating parametric design
Parametric design allows for the establishment of relationships among different design elements using mathematical equations. These relationships make experimenting with different design options easier and automatically adjust all related components when one element changes.
7. Using 4D and 5D BIM
4D BIM incorporates time-related data into the model, making it a valuable tool for project scheduling and management, whereas 5D BIM involves cost data, enabling more accurate cost estimations and better financial management.
8. Implementing virtual reality (VR)
Like AR — virtual reality allows for an engaging 3D representation of BIM models. This can be particularly useful in client presentations, allowing clients to virtually “walk through” the design before construction begins.
9. Applying generative design

Generative design uses AI algorithms to generate multiple design options based on predefined goals and constraints. This can enable more efficient and innovative solutions than traditional design methods.
10. Integrating GIS and BIM
Geographic Information System (GIS) data can be integrated into BIM models to provide contextual geographical and environmental information. This can support more sustainable and contextually appropriate design decisions.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion — harnessing advanced strategies for BIM can significantly enhance the design and construction process, fostering collaboration and driving informed decisions.
As technology evolves, it continues to unlock new potential in the field of architecture and construction.
 Hi Boox Popular Magazine 2025
Hi Boox Popular Magazine 2025